As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, industries around the world are undergoing rapid transformation. Automation and machine learning are reshaping how we work, leading to both excitement and concern about the future of employment. While many routine or data-driven tasks are being handed over to AI, there are certain job categories that experts believe will remain firmly in human hands. These roles rely on complex social interaction, deep emotional intelligence, and creative judgment, all of which are difficult for machines to replicate. Based on current research and expert insights, here are three categories of jobs that AI is unlikely to replace anytime soon.
1. Creative Professions Require Original Human Thought
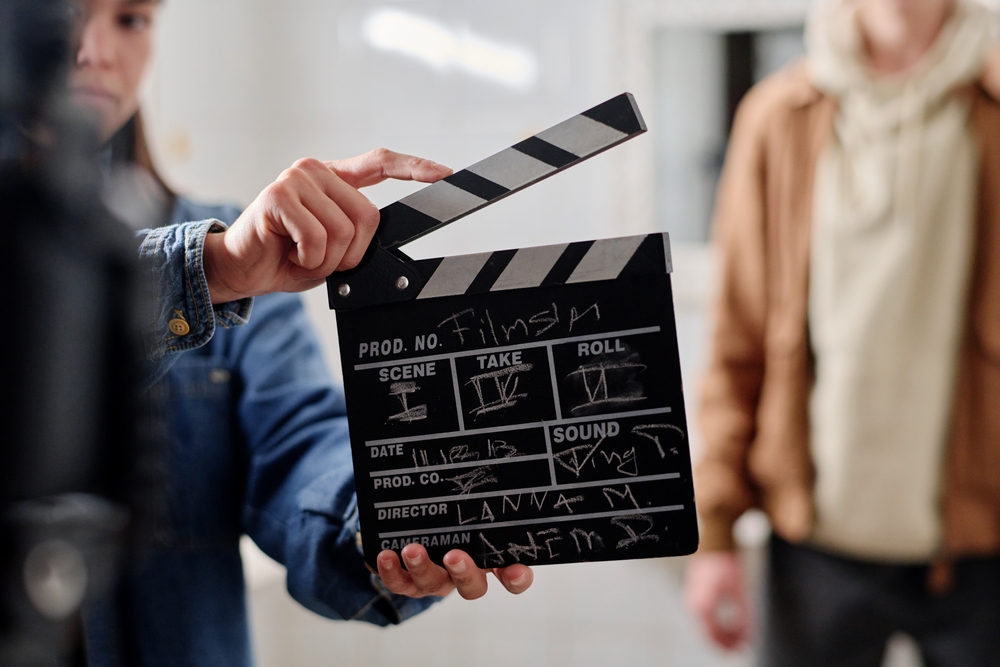

Creativity is one of the most difficult human abilities for AI to replicate. While AI can generate art, music, or writing based on patterns, it cannot originate ideas or infuse them with genuine emotional depth. Jobs in fields such as design, filmmaking, literature, and advertising require more than technical output. They involve intuition, emotional resonance, cultural understanding, and human storytelling. According to researchers at MIT, true creative thinking involves divergent thought and emotional processing that AI lacks. A graphic designer, for example, tailors visual communication to human emotion and context. These subtleties are beyond current AI capabilities, making creativity-driven careers safe from full automation.
2. Healthcare Jobs Demand Human Empathy
Healthcare is a deeply human field, rooted in compassion and trust. While AI can assist with diagnostics or administrative work, core roles such as doctors, nurses, therapists, and social workers require emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills that machines cannot provide. According to the World Health Organization, effective healthcare delivery depends on empathy, communication, and ethical decision-making. Patients do not just want accurate treatment, they want to feel understood and cared for. Human professionals are uniquely able to read body language, comfort anxiety, and build trust. Even the most advanced AI lacks the capacity for human-to-human connection, which is essential for effective care and healing.
3. Education Relies on Human Interaction and Adaptation
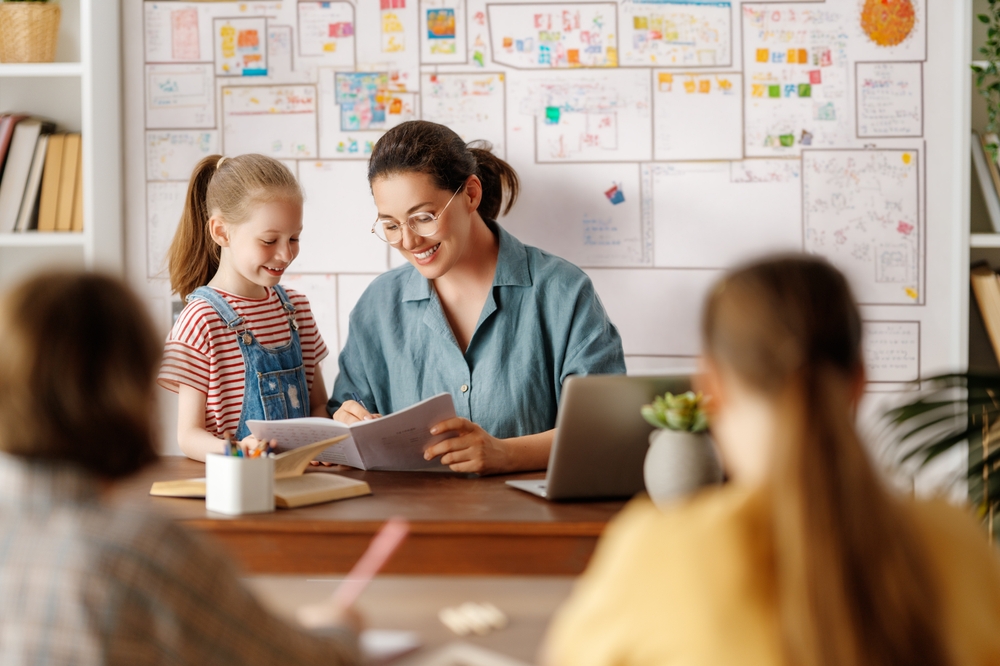

Teaching is not just about delivering information. It is about connecting with students, recognizing their needs, and adapting instruction accordingly. Experts in education technology agree that while AI can support learning through tools and platforms, it cannot replace human educators. Teachers observe behavior, respond to emotional cues, and adjust their approach based on real-time feedback. A good teacher inspires, encourages, and mentors students in ways machines cannot emulate. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization emphasizes that learning is a social process. AI can supplement instruction but lacks the ability to foster relationships or respond to the complex challenges students face inside and outside the classroom.
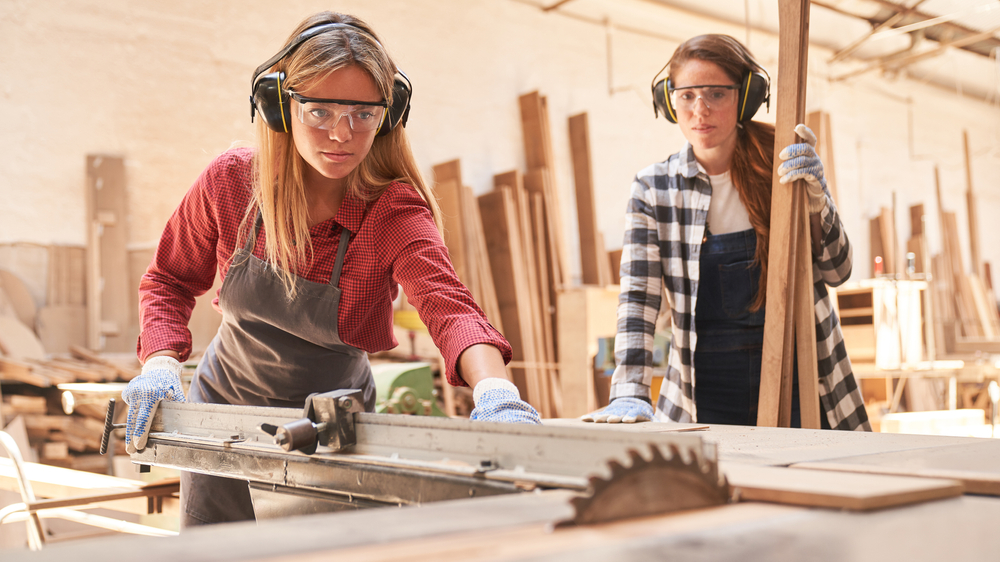
4. Skilled Trades Require Physical Dexterity and Judgment
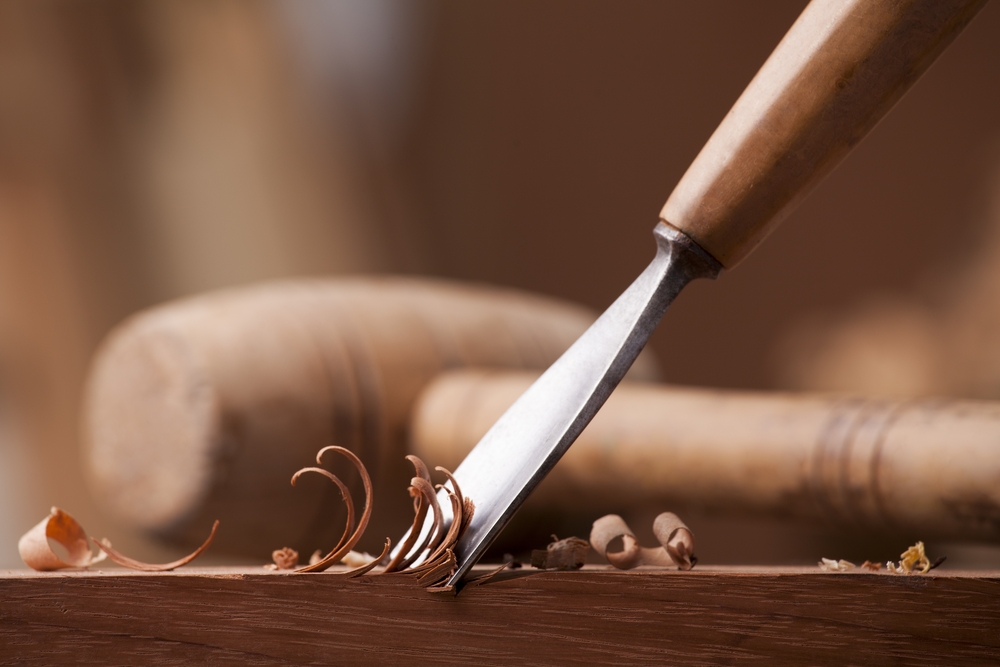

Jobs in skilled trades such as plumbing, electrical work, carpentry, and mechanics require a combination of hands-on expertise and situational problem-solving. These jobs often involve unpredictable environments and unique challenges that require flexible thinking and physical precision. While robots can perform certain manufacturing tasks, they struggle with the adaptability and dexterity needed for fieldwork. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, skilled trade roles are less likely to be automated due to the complex, non-repetitive nature of the work. Tradespeople must assess damage, improvise solutions, and make decisions based on the physical world, all of which require human presence and practical intelligence.
Read More: Robotic Exoskeleton Helps You Go Farther and Move Faster
5. Leadership Roles Involve Strategy and Emotional Intelligence
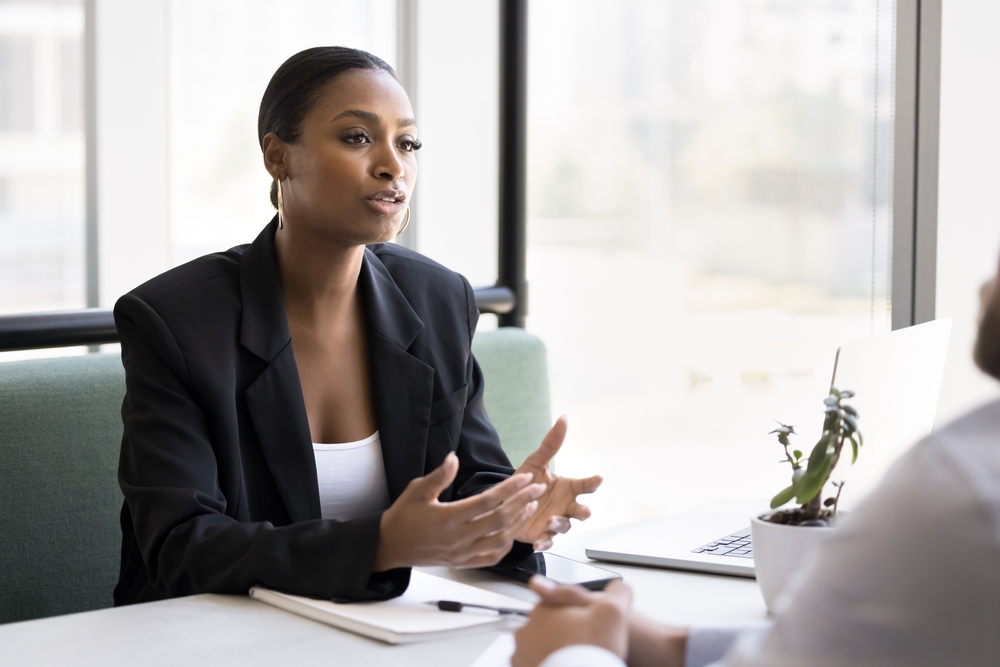

Leadership is not just about decision-making, it is about guiding teams, inspiring people, and managing conflict. These are deeply interpersonal skills that AI cannot replicate. CEOs, managers, and team leaders rely on emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and vision. Research from Harvard Business Review indicates that the most effective leaders balance analytical thinking with empathy and communication. While AI can provide data-driven insights, it cannot motivate or build trust. Human leaders interpret organizational culture, understand team dynamics, and adapt strategies in complex and changing environments. Their ability to connect emotionally and think abstractly places leadership firmly beyond the reach of artificial systems.
6. Mental Health Professions Need Human Presence
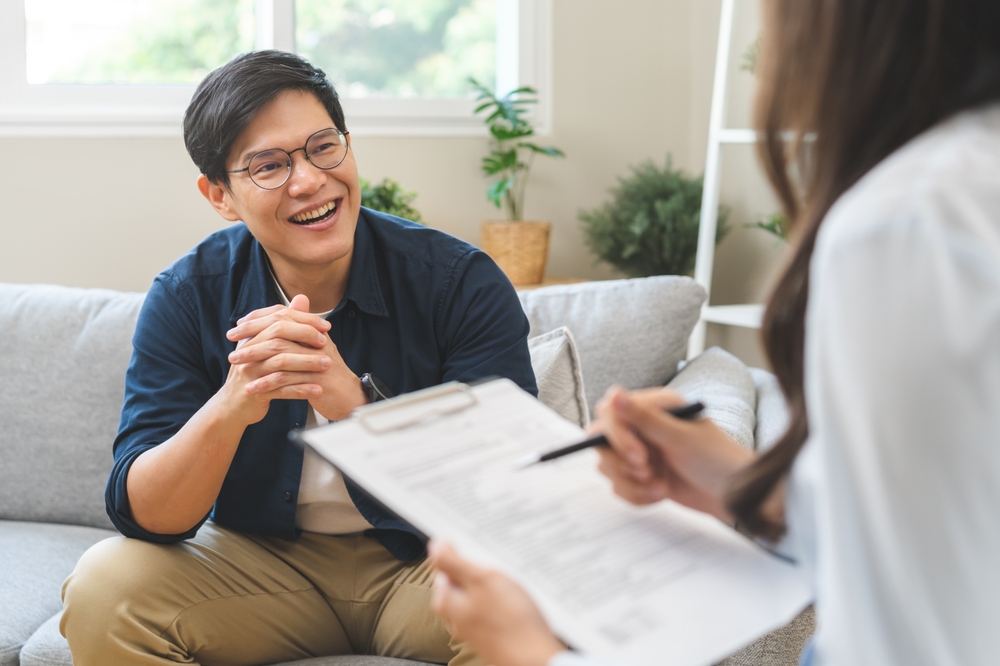

Psychologists, counselors, and therapists work in a field that is entirely dependent on human connection. Mental health treatment requires the ability to listen deeply, interpret emotions, and offer personalized support. AI chatbots can provide basic conversation or crisis management, but they cannot offer the nuanced care that human professionals provide. According to the American Psychological Association, therapeutic relationships are one of the strongest predictors of treatment success. This connection cannot be simulated by software. Human therapists understand subtle shifts in tone, body language, and mood. They provide comfort, validation, and insight, which requires empathy and lived experience. These roles remain essential and irreplaceable.
7. Legal Professionals Use Judgment and Advocacy

Legal work is not only about interpreting laws. It also involves critical thinking, ethical reasoning, and advocating for others. Lawyers, judges, and legal advisors must navigate complex human scenarios, often with moral and social implications. While AI can assist with document review or legal research, it cannot replace the strategic and emotional aspects of legal practice. Legal professionals must argue cases, negotiate deals, and understand human motivations. According to the American Bar Association, the legal field requires nuanced communication and personal judgment that machines cannot provide. Even with advances in legal tech, the need for human advocates and interpreters remains vital.
8. The Human Element Is Irreplaceable

Across all job categories that resist automation, one theme is clear. They depend on the human ability to think creatively, feel empathy, make ethical choices, and build relationships. These are not skills that can be programmed into a machine. Experts agree that while AI will transform many industries, it will not eliminate the need for uniquely human work. The future of employment will likely involve collaboration between humans and machines, not replacement. Jobs that emphasize compassion, originality, and interpersonal connection will remain in high demand. By focusing on these strengths, workers can build careers that are resilient in an increasingly automated world.
Read More: 50 Jobs That AI Will Replace In The Next 5 Years
Final Thoughts

The rise of artificial intelligence is changing how we work, but it is not eliminating the value of human qualities. Jobs that rely on empathy, creativity, critical thinking, and personal connection continue to stand strong in the face of automation. While AI can support and enhance many roles, it lacks the depth of understanding and emotional presence that only humans provide. Experts consistently point to creative fields, healthcare, education, leadership, skilled trades, mental health, and legal work as areas where human input is irreplaceable. As the workforce evolves, focusing on these distinctly human abilities will not only protect careers but also enrich the way we live and work together.
Disclaimer: This article was created with AI assistance and edited by a human for accuracy and clarity.

